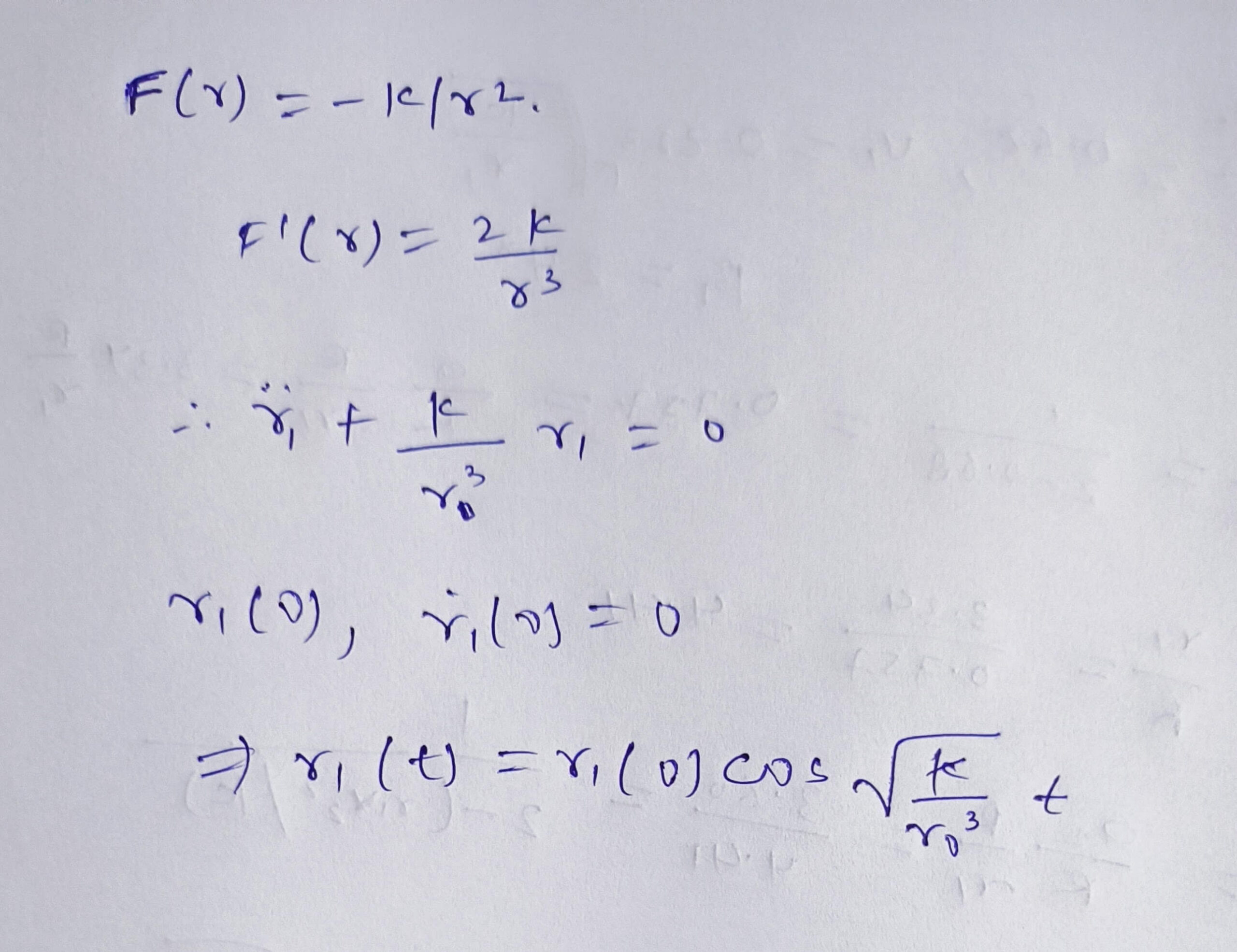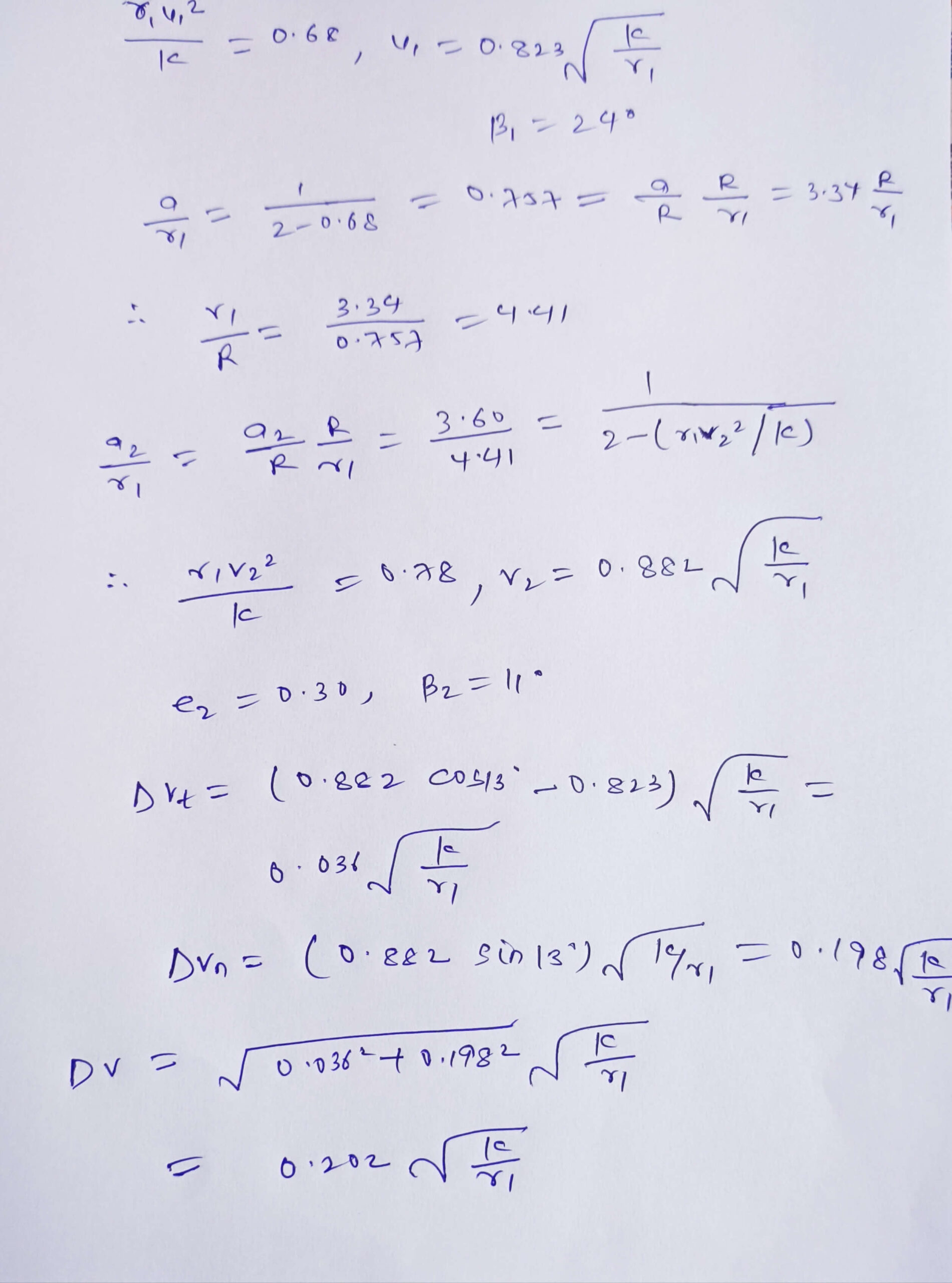624
Points
Questions
72
Answers
119
-
Asked on 13th November 2023 in Aeronautics.
For NACA 2412 angle of attack at 4°, coefficient of lift is nearly 0.65 and coefficient of drag is nearly 0.04.
Lift per unit span is
{L}’ = \frac{1}{2}\rho_{\infty}V^{2}Cc_{l}
{L}’ = \frac{1}{2}\left ( 1.225 \right )\left ( 30 \right )^{2}1.5\left ( 0.65 \right ) = 537.5N/m
Drag per unit span is
{D}’ = \frac{1}{2}\rho_{\infty}V^{2}Cc_{d}
{D}’ = \frac{1}{2}\left ( 1.225 \right )\left ( 30 \right )^{2}1.5\left ( 0.04 \right ) = 33.075N/m
- 618 views
- 1 answers
- 0 votes
-
Asked on 13th November 2023 in Aeronautics.
For steady, level flight, the weight is equal to the lift.
C_{L} = \frac{L}{q_{\infty}S} = \frac{W}{q_{\infty}S}
V_{\infty} = 160\left ( \frac{88}{60} \right )=234.7\,ft/s
q_{\infty} = \frac{1}{2}\rho_{\infty} V_{\infty}^{2} = \frac{1}{2}\left ( 0.002377 \right )\left ( 234.7 \right )^{2} = 65.45\,lb/ft^{2}Therefore,
C_{L} = \frac{W}{q_{\infty}S}= \frac{506000}{\left ( 65.45 \right )\left (4605 \right )} = 0.362
- 635 views
- 1 answers
- 0 votes
-
Asked on 9th November 2023 in Flight mechanics.
Moment arm = 0.3c – 0.25c = 0.05c
M_{c/4} = -(0.05c)(200) = -10c = -10(5) = -50 ft-lb\, \textrm {per unit span}
The moment about the leading edge point is given by the lift acting through the center of pressure, with a moment arm 0.3c,
M_{LE} = -(0.3)(200) = -60c = -60(5) = -300 ft-lb\, \textrm{per unit span}
- 653 views
- 1 answers
- 0 votes
-
Asked on 8th November 2023 in Space dynamics.
- 834 views
- 1 answers
- 0 votes
-
Asked on 8th November 2023 in Space dynamics.
- 531 views
- 1 answers
- 0 votes
-
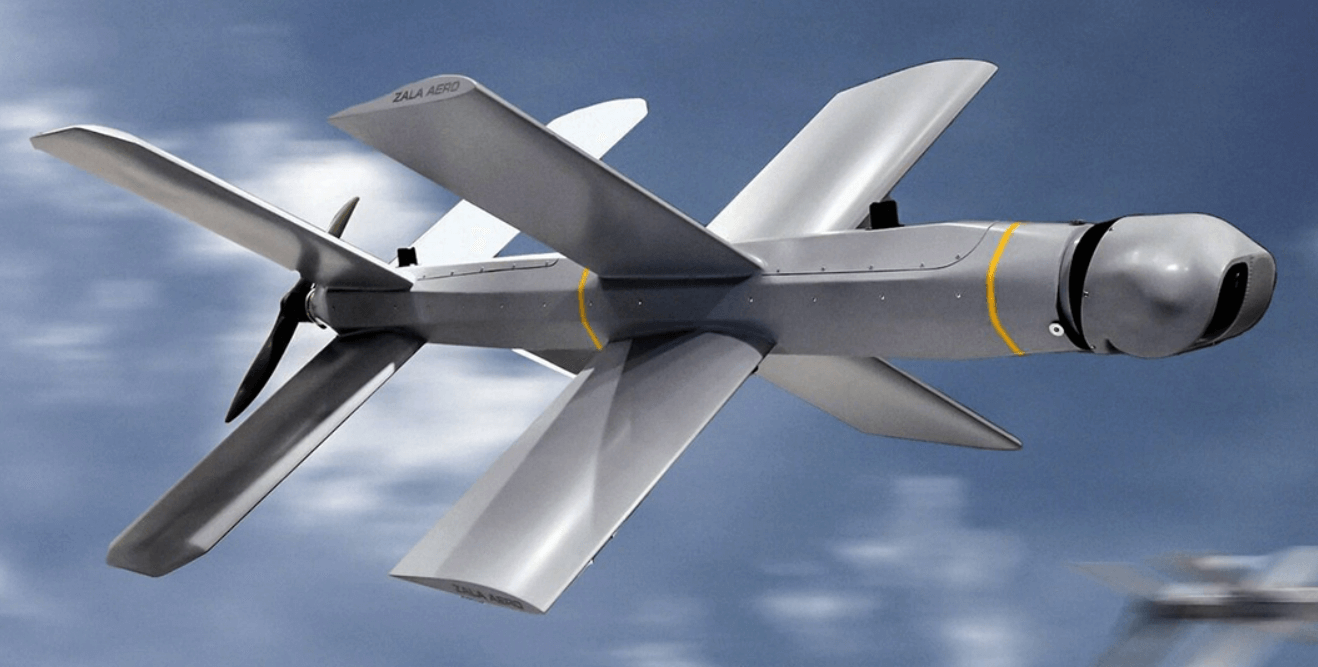
Asked on 13th June 2023 in UAV.
Switchblade is a small or miniature loitering munition developed by AeroVironment. It is mostly used by the United States army and also used in the Russian – Ukrainian war. Switchblades can be carried by the army by using a backpack. Switchblade gets launched from a tube and then flies to the target where it detonates by using an explosive warhead. There are two variants of Switchblade 300 and 600.
Switchblade is used for long range targets. It has the capability of identifying, tracking and engaging the targets as well as to follow a pre-programmed line of path. Switchblade 300 is designed to destroy light armored vehicles and can also be made to retarget en-route. It is very small and does not produce noise and does not have any heat signature which makes it very difficult to identify and intercept.
Switchblade 600 is similar to 300 and it is portable and can be set up in 10 minutes. It can fly up to 40 km in 20 minutes and after that loiter for next 20 minutes giving it a maximum range of 80 km. It can strike a target at a speed of 185 km/h. Its GPS system provides situational awareness, information collection, object and target recognition. It is propelled by an electric battery and a propeller located at the back. It has a two tandem piercing warhead and can also destroy tanks with reactive armour.
So, a Switchblade 600 can destroy a tank. It has two warheads. The first one destroys the reactive armour which is meant in the tank to counteract RPG or missiles and the second warhead destroys the tank.
Since the Switchblades work on GPS for its location and navigation, it can be jammed and its operation can be disrupted. Also it has a range of only 40 km and an endurance of 20 minutes. Also for utilizing its long range capabilities of 80 km it requires two antennas to be deployed in the field for relaying command from one operator to another through data link.
- 694 views
- 1 answers
- 0 votes
-
Asked on 9th June 2023 in UAV.
Loitering munition as the name suggests is a munition which loiters on any target and then makes a hit. This was first tested or used in 1944 by the Japanese special attack unit of military aviators. This type of suicide aircrafts are also called Kamikaze and this is a Japenese word with its literal meaning as divine or spirit wind.
This warcraft is a combination between UCAV and missile. On seeing at a first glance we can infer that it is a cruise missile having wings. This type of weaponry system falls in between the above two categories. It is similar to the cruise missile but has the capability to loiter on any target for a considerable amount of time. Unlike UCAV it has inbuilt warhead.
Loitering munition examples are IAI Harpy, skyStriker, Warmate, Switchblade, Trinetra, Nagastra, Raytheon Coyote.
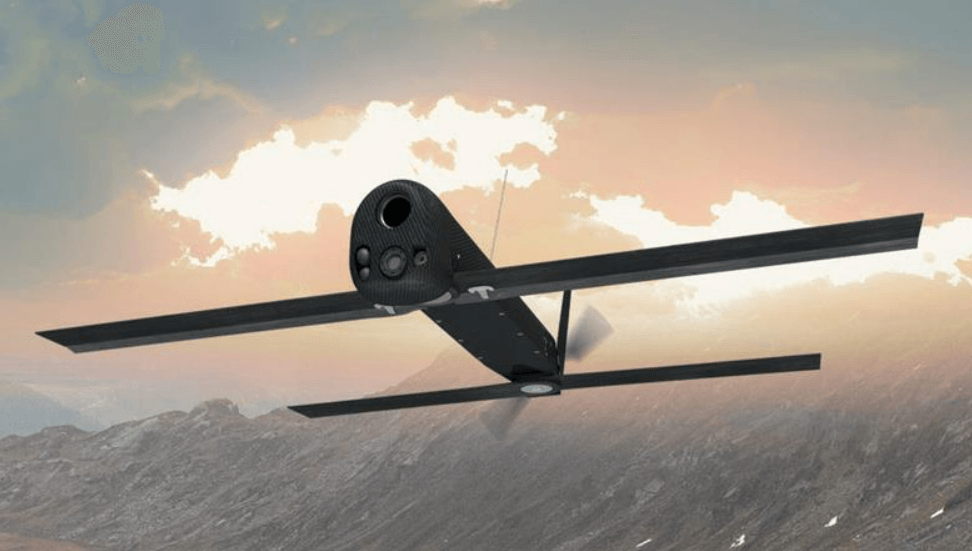 Switchblade loitering munition
Switchblade loitering munitionThese type of suicide drones were first made in 1980s but the term loitering munition was not used. From the 2000s these types of drones were made to have extra capabilities, there were improvements in design as well as some advanced technologies were added.
Loitering munitions are used by both Russia and Ukraine at present and have found success in disrupting the armed forces.
These type of drones can be countermeasured by making cages of chain link fencing, wire mesh and wooden logs around the target which confuses it. Inflatable decoys and wooden vehicles can also be used to confuse these drones. These drones can also be shootout by rifles. Electronic warfare systems can also be used to stop the drone by jamming the GPS and radio links. A slat armor can also be used around vehicles as these drones have a less powerful warhead.
- 749 views
- 1 answers
- 0 votes
-
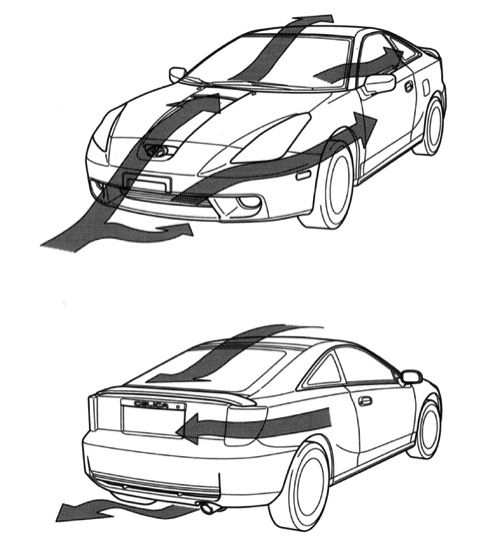
Asked on 11th May 2023 in Aerodynamics.
Aerodynamics is the study of flow of air over any object. It is the study of dynamics of air. Any object which undergoes any motion has an aerodynamic effect in it. We can harness the power of air through aerodynamics. In general aerodynamics has a degrading feature which is called drag.
Drag opposes the motion of the object or the vehicle. So, there will be more consumption of fuel by the engine in order to overcome this drag. The amount of drag increases with the speed. So car designers need to design cars in such a way that there should be a minimum effect of drag. There is also one effect of aerodynamic forces, which is lift. For the aircraft lift is useful, as it makes the aircraft fly in the sky. However, for the case of a car, it is not useful. The air which is blowing beneath the car can uplift the vehicle when the car is moving at a very high speed.
So, with respect to a car we need to see both lift and drag. Nowadays cars are designed which are of aerodynamic design. Aerodynamic design means the car is designed to overcome both lift and drag forces or to utilize it for the enhancement of car performance. Cars are now made of streamlined shape. By streamline means there is a smooth flow of air over the car body. When there is a smooth flow of air and no restriction to it, then there is a very less creation of drag force. We have cars with door handles and wipers as well as flush headlights and glasses designed in such a way that it provides least resistance to the flow of air. So now in a car there is more concentration on its design with every detail. Similarly bumpers with spoilers are provided in order to channelize the flow of air beneath the car and create a downforce such that the car does not leave the ground at a very high speed. Similarly a rear wing is also present in racing cars in order to create a downward force at high speeds. These are adjustable which means it can move up and down in order to adjust and create the required downforce.
Earlier designs of the cars used to have a blunt body. A blunt body can create a huge amount of drag. At lower maximum speed of cars this does not create a significant amount of drag, however at high speed it can create substantial amount of drag and can affect the performance of cars.
So this is how aerodynamics work on a car.
- 950 views
- 1 answers
- 0 votes
-
Asked on 9th May 2023 in Aerodynamics.
Aerodynamics is the study of dynamics of air. When there is a flow of air over any object, then there is a creation of lift force as well as drag force. These two forces are a result of pressure differences which are created due to flow of air over the top and bottom surface of the body and also due to shear stress on the surface of the body. However, a major contribution is of forces which are created due to pressure difference. These forces are normal and perpendicular to the flow direction.
The force which is perpendicular to the flow direction is lift force. The force which is parallel to the air flow is drag force. Lift force and drag force are both related to a coefficient, which plays a major role in calculation of these two forces. These coefficients are called lift coefficient and drag coefficient.
Lift and drag forces are proportional to the surface area, density and velocity of air. Formula to calculate the lift coefficient is
{c_l} = \frac{L}{{q_\infty }S}
and to calculate drag coefficient is
c_d =\frac{D}{{q_\infty }S}
Lift force makes any object fly. It uplifts the object from the ground. Drag force opposes the motion of the object. In order to overcome this drag force there needs to be some counteracting force. The engine of the vehicles as well as of the aircraft opposes the drag force and makes the vehicle as well as aircraft move forward. Similarly lift is balanced by weight. Lift is a good force for aircrafts and helicopters, however it is a degrading force for racing cars and vehicles.
There are different types of drag force like induced drag, pressure drag and skin friction drag and drag at supersonic speed which is wave drag. We can also calculate these drags.
Coefficient of Induced drag can be calculated as
C_{D,i}=\frac{C_{L}^{2}}{\pi e AR}
Coefficient of lift at supersonic speed and wave drag coefficient can be calculated as,
c_{l}=\frac{4\alpha }{\sqrt{M_{\infty}^{2}-1}}
c_{d}=\frac{4\alpha ^{2}}{\sqrt{M_{\infty}^{2}-1}}
this is with respect to a flat plate at supersonic speed.
- 915 views
- 1 answers
- 0 votes
-
Asked on 5th May 2023 in Aerodynamics.
Aerodynamics is the study of flow of air over any object and the flow of air over any object can generate forces. These forces are lift and drag. Lift is the force which tries to lift any object from the ground. Drag opposes the forward motion. Lift can be considered as a supporting force for aircrafts and degrading force for vehicles, particularly racing vehicles, whereas drag can be considered as a degrading force for both aircrafts and vehicles. Sometimes drag is useful to reduce greater speed in a racing vehicle.
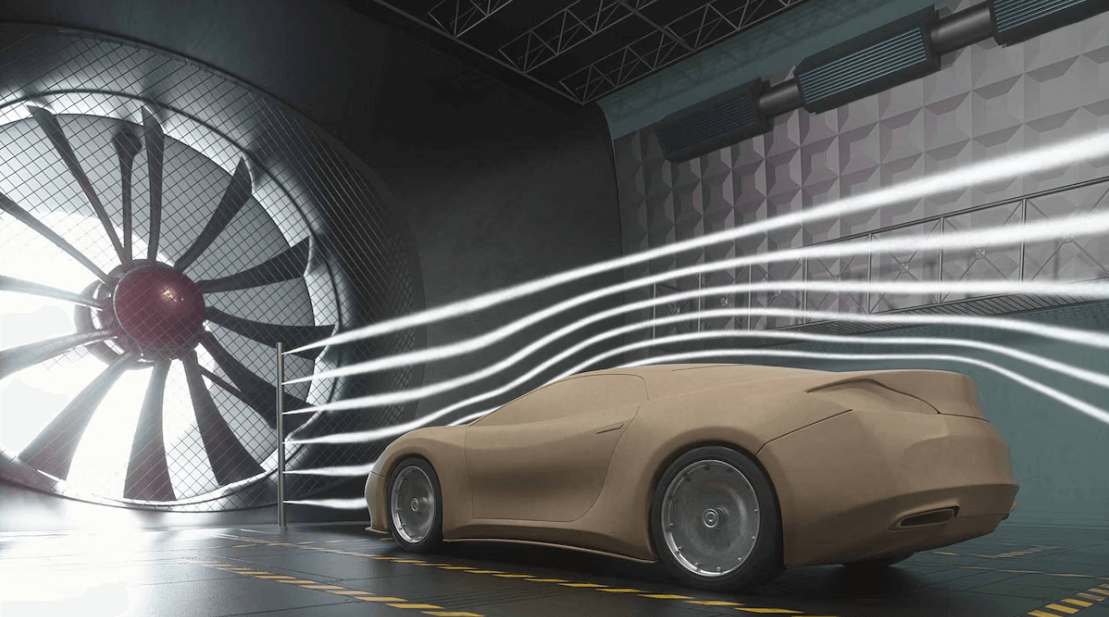
We are using wind tunnels in order to test or visualize airflow and measure aerodynamic forces. These forces are measured using various probes which are placed at different points in the wind tunnel. The probes can also be put on objects in order to measure the forces.
Nowadays in order to measure aerodynamic forces there are uses of pressure sensors and force sensors. These sensors provide more accurate readings. After getting the readings, we can use it to measure coefficient of lift as well as coefficient of drag. These coefficients are used in order to measure the lift as well as the drag force.
Aerodynamics can also be measured by the use of computational fluid dynamics or CFD. There are many simulation software which can predict near accurate aerodynamic results using CFD. These are more cost efficient and less time consuming than carrying out wind tunnel tests.
Aerodynamics can also be measured in real life, like while using our own vehicle and measuring the drag force using some devices. These are not accurate and can differ on different situations, like weather condition, traffic and condition of the track or road.
- 878 views
- 1 answers
- 0 votes