How to measure aerodynamics ?
How to measure aerodynamics ?
Aerodynamics is the study of flow of air over any object and the flow of air over any object can generate forces. These forces are lift and drag. Lift is the force which tries to lift any object from the ground. Drag opposes the forward motion. Lift can be considered as a supporting force for aircrafts and degrading force for vehicles, particularly racing vehicles, whereas drag can be considered as a degrading force for both aircrafts and vehicles. Sometimes drag is useful to reduce greater speed in a racing vehicle.
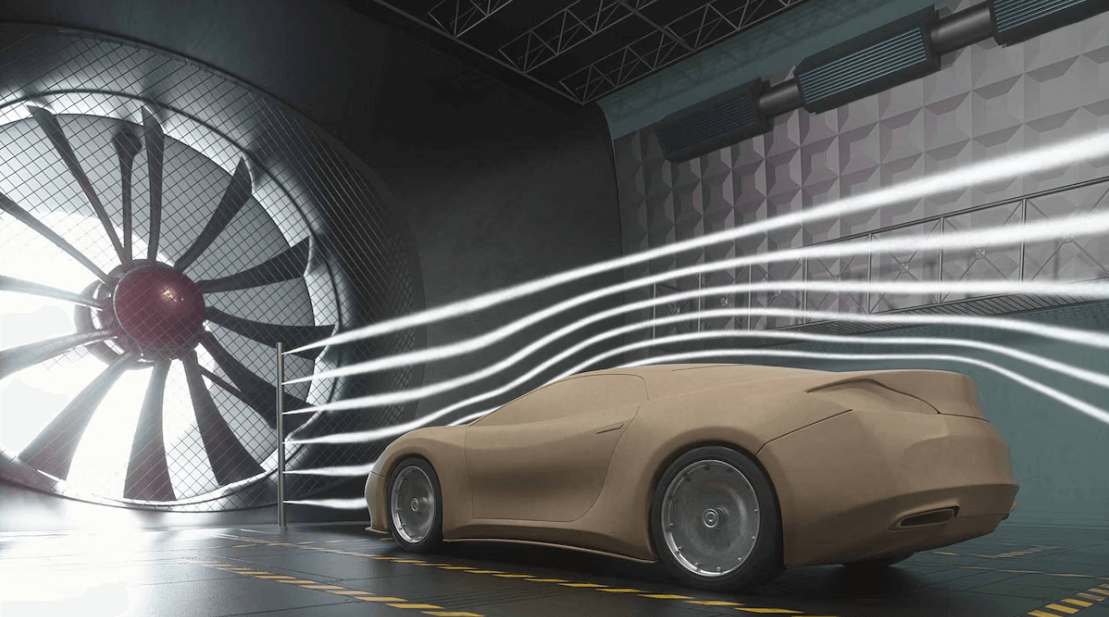
We are using wind tunnels in order to test or visualize airflow and measure aerodynamic forces. These forces are measured using various probes which are placed at different points in the wind tunnel. The probes can also be put on objects in order to measure the forces.
Nowadays in order to measure aerodynamic forces there are uses of pressure sensors and force sensors. These sensors provide more accurate readings. After getting the readings, we can use it to measure coefficient of lift as well as coefficient of drag. These coefficients are used in order to measure the lift as well as the drag force.
Aerodynamics can also be measured by the use of computational fluid dynamics or CFD. There are many simulation software which can predict near accurate aerodynamic results using CFD. These are more cost efficient and less time consuming than carrying out wind tunnel tests.
Aerodynamics can also be measured in real life, like while using our own vehicle and measuring the drag force using some devices. These are not accurate and can differ on different situations, like weather condition, traffic and condition of the track or road.