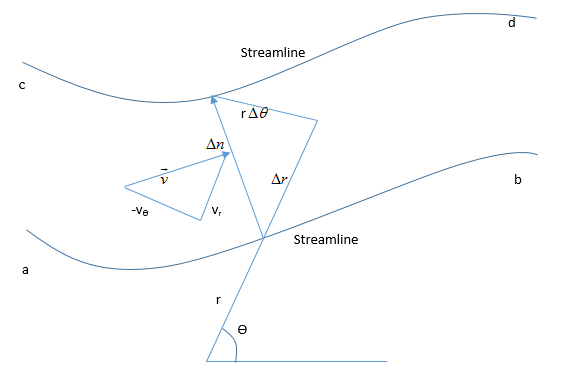
Consider a flow field in polar coordinates, where the stream function is given as ψ = ψ(r, θ). Starting with the concept of mass flow between two streamlines, derive Equations \rho V_{r}=\frac{1}{r}\frac{\partial \bar{\psi }}{\partial \theta} and \rho V_{\theta}=-\frac{\partial\bar{\psi} }{\partial r}.
Consider a flow field in polar coordinates, where the stream function is given as ψ = ψ(r, θ). Starting with the concept of mass flow between two streamlines, derive Equations \rho V_{r}=\frac{1}{r}\frac{\partial \bar{\psi }}{\partial \theta} \\\rho V_{\theta}=-\frac{\partial\bar{\psi} }{\partial r}
\psi =\psi\left ( r,\theta \right )
Mass flow between streamlines =\Delta \bar {\psi} \Delta \bar{\psi}=\rho V \Delta n \\\Delta \bar {\psi} = \left ( -\rho V_{\theta} \right ) \Delta r+\rho V_{r}\left ( r\theta \right )
Let ‘cd’ approaches ‘ab’:
d\bar{\psi}=-\rho V_{\theta}dr+\rho rV_{r}d\theta
Also, since \bar{\psi}=\bar{\psi}\left ( r,\theta \right ),from calculus d\bar{\psi}=\frac{\partial \bar{\psi}}{\partial r}dr+\frac{\partial \bar{\psi}}{\partial \theta}d\theta
On comparing -\rho V_{\theta}=\frac{\partial \bar{\psi}}{\partial r} and \rho r V_{r}=\frac{\partial \bar{\psi }}{\partial \theta}
or \rho V_{r}=\frac{1}{r}\frac{\partial \bar{\psi}}{\partial \theta} and \rho V_{\theta}=-\frac{\partial\bar{\psi} }{\partial r}